Router Transformation
Router Transformation in Informatica
Router transformation is an active and connected transformation. It is similar to the filter transformation used to test a condition and filter the data. In a filter transformation, you can specify only one condition and drops the rows that do not satisfy the condition. Where as in a router transformation, you can specify more than one condition and provides the ability for route the data that meet the test condition. Use router transformation if you need to test the same input data on multiple conditions.
Creating Router Transformation
Follow the below steps to create a router transformation
Configuring Router Transformation
The router transformation has input and output groups. You need to configure these groups.
User-defined groups: Create a user-defined group to test a condition based on the incoming data. Each user-defined group consists of output ports and a group filter condition. You can create or modify the user-defined groups on the groups tab. Create one user-defined group for each condition you want to specify.
Default group: The designer creates only one default group when you create one new user-defined group. You cannot edit or delete the default group. The default group does not have a group filter condition. If all the conditions evaluate to FALSE, the integration service passes the row to the default group.
Specifying Group Filter Condition
Specify the group filter condition on the groups tab using the expression editor. You can enter any expression that returns a single value. The group filter condition returns TRUE or FALSE for each row that passes through the transformation.
Advantages of Using Router over Filter Transformation
Use router transformation to test multiple conditions on the same input data. If you use more than one filter transformation, the integration service needs to process the input for each filter transformation. In case of router transformation, the integration service processes the input data only once and thereby improving the performance.
Router Transformation Examples
1. Create the employees data into two target tables. The first target table should contain employees with department_id 10 and second target table should contain employees with department_id 20?
Solution: connect the source qualifier transformation to the router transformation.
In the router transformation, create two output groups. Enter the below filter conditions.
Now connect the output groups of router transformation to the targets
2. The router transformation has the following group filter conditions.
What data will be loaded into the first and second target tables?
Solution: The first target table will have employees from department 30. The second table will have employees whose department ids are less than or equal to 30.
Creating Router Transformation
Follow the below steps to create a router transformation
- In the mapping designer, create a new mapping or open an existing mapping
- Go the toolbar->Click on Transformation->Create
- Select the Router Transformation, enter the name, click on create and then click on Done.
- Select the ports from the upstream transformation and drag them to the router transformation. You can also create input ports manually on the ports tab.
Example: If we want to keep employees of France, India, US in 3 different tables,then we can use 3 Filter transformations or 1 Router transformation.
Mapping A uses three Filter transformations while Mapping B produces the same result with one Router transformation.
A Router transformation consists of input and output groups, input and output ports, group filter conditions, and properties that we configure in the Designer.
Working with Groups
A Router transformation has the following types of groups:
- Input: The Group that gets the input ports.
- Output: User Defined Groups and Default Group. We cannot modify or delete Output ports or their properties.
User-Defined Groups: We create a user-defined group to test a condition based on incoming data. A user-defined group consists of output ports and a group filter Condition. We can create and edit user-defined groups on the Groups tab with the Designer. Create one user-defined group for each condition that we want to specify.
The Default Group: The Designer creates the default group after we create one new user-defined group. The Designer does not allow us to edit or delete the default group. This group does not have a group filter condition associated with it. If all of the conditions evaluate to FALSE, the IS passes the row to the default group.
Example: Filtering employees of Department 10 to EMP_10, Department 20 to EMP_20 and rest to EMP_REST
- Source is EMP Table.
- Create 3 target tables EMP_10, EMP_20 and EMP_REST in shared folder. Structure should be same as EMP table.
- Create the shortcuts in your folder.
Creating Mapping:
1. Open folder where we want to create the mapping.
2. Click Tools -> Mapping Designer.
3. Click Mapping-> Create-> Give mapping name. Ex: m_router_example
4. Drag EMP from source in mapping.
5. Click Transformation -> Create -> Select Router from list. Give name and
Click Create. Now click done.
6. Pass ports from SQ_EMP to Router Transformation.
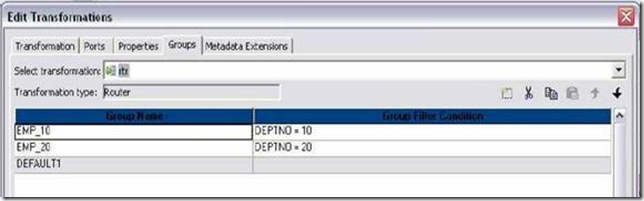
7. Edit Router Transformation. Go to Groups Tab
8. Click the Groups tab, and then click the Add button to create a user-defined Group. The default group is created automatically..
9. Click the Group Filter Condition field to open the Expression Editor.
10. Enter a group filter condition. Ex: DEPTNO=10
11. Click Validate to check the syntax of the conditions you entered.
12. Create another group for EMP_20. Condition: DEPTNO=20
13. The rest of the records not matching the above two conditions will be passed to DEFAULT group. See sample mapping
14. Click OK -> Click Apply -> Click Ok.
15. Now connect the ports from router to target tables.
16. Click Mapping -> Validate
17. Repository -> Save
- Create Session and Workflow as described earlier. Run the Workflow and see the data in target table.
- Make sure to give connection information for all 3 target tables.
Sample Mapping:
Difference between Router and Filter :
We cannot pass rejected data forward in filter but we can pass it in router. Rejected data is in Default Group of router.
Configuring Router Transformation
The router transformation has input and output groups. You need to configure these groups.
- Input groups: The designer copies the input ports properties to create a set of output ports for each output group.
- Output groups: Router transformation has two output groups. They are user-defined groups and default group.
User-defined groups: Create a user-defined group to test a condition based on the incoming data. Each user-defined group consists of output ports and a group filter condition. You can create or modify the user-defined groups on the groups tab. Create one user-defined group for each condition you want to specify.
Default group: The designer creates only one default group when you create one new user-defined group. You cannot edit or delete the default group. The default group does not have a group filter condition. If all the conditions evaluate to FALSE, the integration service passes the row to the default group.
Specifying Group Filter Condition
Specify the group filter condition on the groups tab using the expression editor. You can enter any expression that returns a single value. The group filter condition returns TRUE or FALSE for each row that passes through the transformation.
Advantages of Using Router over Filter Transformation
Use router transformation to test multiple conditions on the same input data. If you use more than one filter transformation, the integration service needs to process the input for each filter transformation. In case of router transformation, the integration service processes the input data only once and thereby improving the performance.
Router Transformation Examples
1. Create the employees data into two target tables. The first target table should contain employees with department_id 10 and second target table should contain employees with department_id 20?
Solution: connect the source qualifier transformation to the router transformation.
In the router transformation, create two output groups. Enter the below filter conditions.
In the first group filter condition,
department_id=10
In the second group filter condition,
department_id=20
Now connect the output groups of router transformation to the targets
2. The router transformation has the following group filter conditions.
In the first group filter condition,
department_id=30
In the second group filter condition,
department_id<=30
What data will be loaded into the first and second target tables?
Solution: The first target table will have employees from department 30. The second table will have employees whose department ids are less than or equal to 30.






























No Comment to " Router Transformation "